The Future of Screw Jacks: Trends and Developments provides an in-depth study of this industry with all essential data. It includes first-hand accounts from industry professionals as well as input from end users themselves.
The global Screw Jacks market is anticipated to experience significant expansion over the forecast period, thanks to a robust auto industry driving sales of these products.
Hydraulics versus Electro-Mechanical Systems
When it comes to lifting and moving heavy loads, both hydraulics and electro-mechanical systems have their advantages and disadvantages. Hydraulics systems typically offer greater power and speed, while electro-mechanical systems tend to be more precise and controllable. However, within the category of electro-mechanical systems, there are many different types of equipment available, each with its unique features and benefits. One such example is the screw jack, which uses a rotating screw to raise or lower a load. Screw jack types can be classified into several types based on their design, including machine screw jacks, ball screw jacks, and worm gear screw jacks. Each type has its own set of advantages, such as higher efficiency, better load distribution, or improved accuracy. Ultimately, the choice between hydraulics and electro-mechanical systems, as well as the specific type of electro-mechanical equipment to use, will depend on the specific application requirements and constraints.
Hydraulic and electromechanical systems are widely utilized across industries for performing an assortment of tasks. Each system comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages; there is no universally suitable option available.
Hydraulic systems transfer power by employing incompressible fluid (usually oil) that flows between piston and cylinder along a piston axis. Pumps apply pressure to increase fluid pressure, in turn moving the cylinder.
Electro-mechanical actuators use electric motors to provide linear force and torque. Energy consumption occurs only when driving loads to their intended positions.
Electromechanical systems offer several distinct advantages over their hydraulic counterparts, including no maintenance requirements and reduced leaks and maintenance requirements.
Electromechanical systems tend to be quieter and easier to clean up, which are both key concerns in the Entertainment Industry where noise control and cleanliness are major considerations.
Hydraulic systems also require more space than electro-mechanical ones to accommodate components like the cylinder, pumps, release valves, filters, hoses and fittings; additional components like motors, data collection sensors or servo systems could further increase its footprint and cost.
Electro-Mechanical Systems versus Hydraulics
Hydraulic systems are commonly used to move objects or control equipment at high-power applications, including heavy machinery and aircraft such as hydraulic presses or wing flaps.
Electro-mechanical systems offer several advantages over hydraulics:
Electric actuators require less energy to operate than hydraulic systems; energy usage occurs only during work.
Additionally, these fans run more quietly and are unaffected by dusty environments – perfect for use in clean rooms.
These features make industrial applications the ideal setting for their application: more resistant to temperature variations, easily controlled for smooth movement and convenient setup.
However, they do come with one major drawback: They’re less accurate than hydraulic systems and therefore cannot achieve precise actuation when clearances between screws and nuts exist.
Anti-backlash control is integral to increasing the precision of screw jacks, as it ensures clearances between screws do not cause backlash when loads are moved in either direction, leading to premature wear or other accuracy issues with these tools.
Electro-Mechanical Systems versus Electro-Mechanical Systems
Electro-mechanical systems (EMSs) are devices which convert mechanical movement into electricity for use by motors or generators, typically for running motors and generators. Additionally, electro-mechanical devices may also be found in renewable energy sources like wind and hydropower production.
These devices are often employed in medical equipment to power motors. Furthermore, they’re frequently seen used in military equipment.
When selecting a screw jack for their motion system, designers and engineers must take into account various factors including load requirements, duty cycles and travel speeds to select an ideal type.
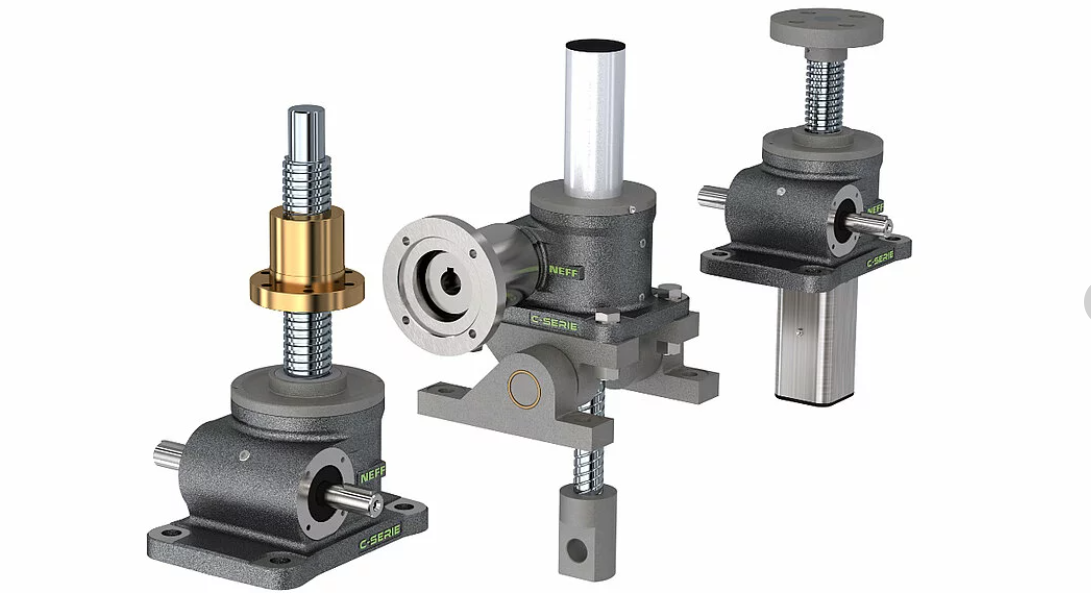
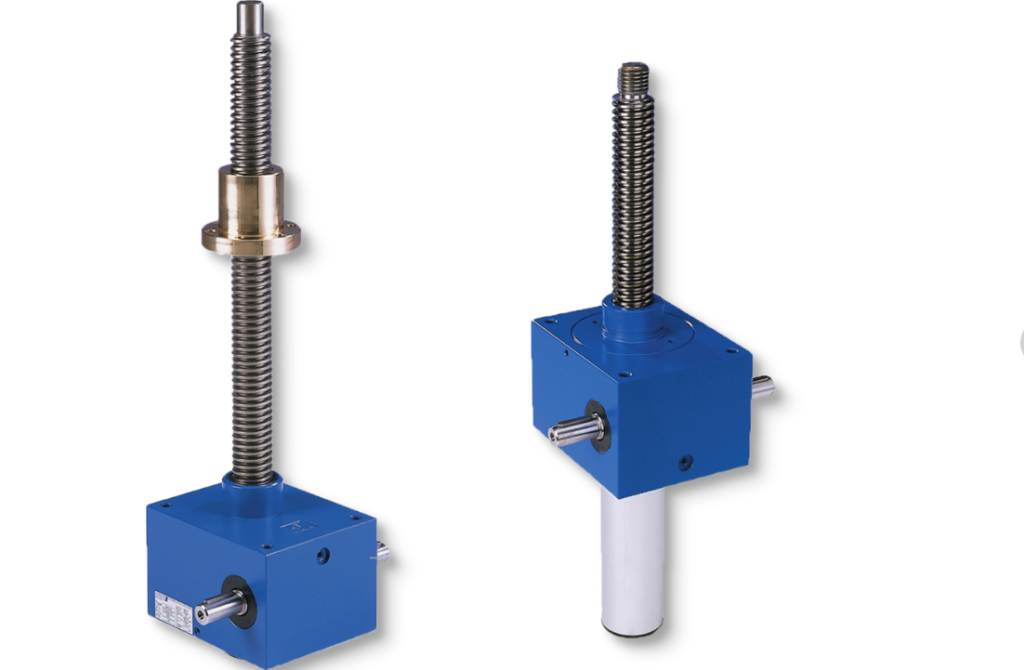
Machine screw jacks and ball screw jacks are two primary forms of screw jacks, both using a worm gear configuration to transform motor or manual input energy into linear motion.
A ball screw jack operates unidirectionally while machine screw jacks move bidirectionally with constant load on their screw threads for greater efficiency in applications that require constant actuation.
Selecting the proper electric screw jack requires understanding how much torque is necessary at all times and considering its load capacity with respect to starting and breakaway forces and static friction, among others. A jack should therefore be selected that limits these torques.